Orthopedic Exam / Special Tests for Physical Therapy: Feet
Causes of Pes Planus/ Flat Foot:
Signs and Symptoms:
People who have flat feet rarely have symptoms or problems. Some people may have pain because of: Changes in work environment, Minor injury, Sudden weight gain, Excessive standing, walking, jumping, or running, Poorly fitted footwear.
Special Test: Functional or Structural Pes Planus Test
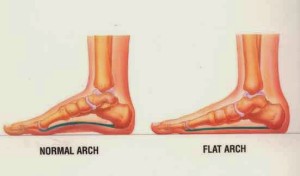
Special Test: Functional or Structural Pes Planus PROCEDURE:
• Therapist observes ( and compares) the orientation of the client’s medial longitudinal arch while doing each of the following:
a. Patient stands straight with both heels and toes on the ground
b. Patient stands with just the toes on the ground
c. Patient sits on the table
Special Test: Functional or Structural Pes Planus POSITIVE TEST:
• Functional Pes Planus = if medial longitudinal arch is restored when the client is either standing on the toes or seated = due to muscle or ligament weakness
• Structural Pes Planus = if medial longitudinal arch remains flat when the client is standing on toes and when seated.
Treatment:
Treatment in adults generally consists of wearing spacious, comfortable shoes with good arch support. Your doctor may recommend padding for the heel (heel cup) or orthotic shoe devices, which are molded pieces of rubber, leather, metal, plastic, or other synthetic material that are inserted into a shoe. They balance the foot in a neutral position and cushion the foot from excessive pounding.
For children, treatment using corrective shoes or inserts is rarely needed, as the arch usually develops normally by age 5.Surgery is rarely needed. You may be able to relieve heel pain by stretching tight calf muscles.